Part 2: Using AI to Improve Requirements—BRDs, User Stories, and Use Cases
Scot Campbell #requirements #quality-assurance #machine learning #continuous-improvement #technology #GIGO #status-reporting #project-governance #project-management #AI #machine-learning #AI in project management #agileProject requirements are the DNA of successful product development, forming the foundation for everything from project timelines to team roles. But in practice, requirements documents like Business Requirements Documents (BRDs), user stories, and use cases are often plagued by vagueness, inconsistency, and even critical omissions. This challenge is especially present in agile environments, where requirements evolve quickly, and the pressure to produce lean, adaptable documentation can sometimes lead to gaps that end up derailing projects.

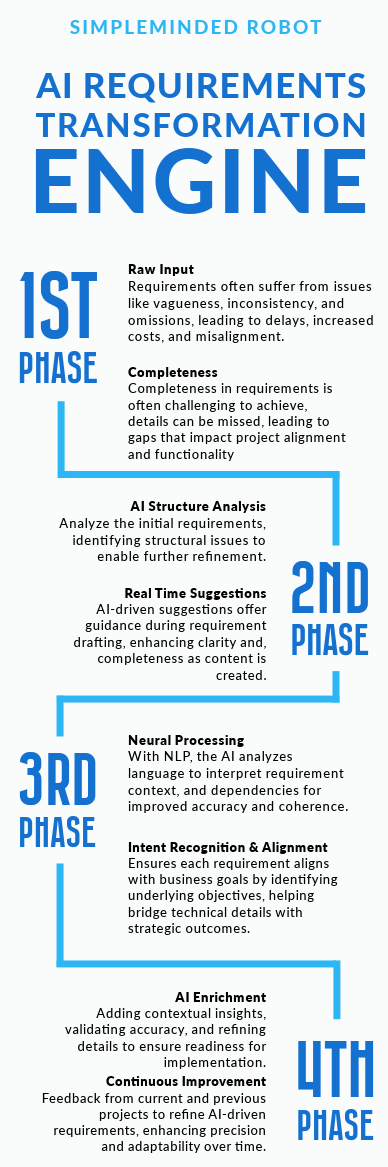
With AI-powered tools, however, we have the potential to address these gaps at the source. By leveraging natural language processing (NLP) and large language models (LLMs), we can elevate the quality of these requirements documents by providing real-time feedback, detecting missing components, and suggesting ways to improve clarity and alignment with business goals.
AI tools bring two key benefits to requirements management: they can check your existing documentation for quality and gaps, while also helping to fill in missing details where needed. This lets project teams focus their expertise where it matters most—on those critical Quality Requirements (QR) that need real human insight and domain knowledge. Instead of getting bogged down documenting every possible scenario and edge case, teams can let AI handle the comprehensive coverage while they concentrate on requirements that directly drive business value and core functionality.
Here’s a practical example: while your team is hammering out complex business rules for a financial trading system, AI can work in parallel to analyze existing requirements and flesh out documentation for supporting features like user authentication, logging, and error handling. It’s like having a capable assistant who ensures nothing falls through the cracks while you focus on the challenging parts. This teamwork between human expertise and AI support gives you both depth in critical areas and solid coverage across the whole requirements landscape.
The Current State of Requirements: A Case for AI Intervention
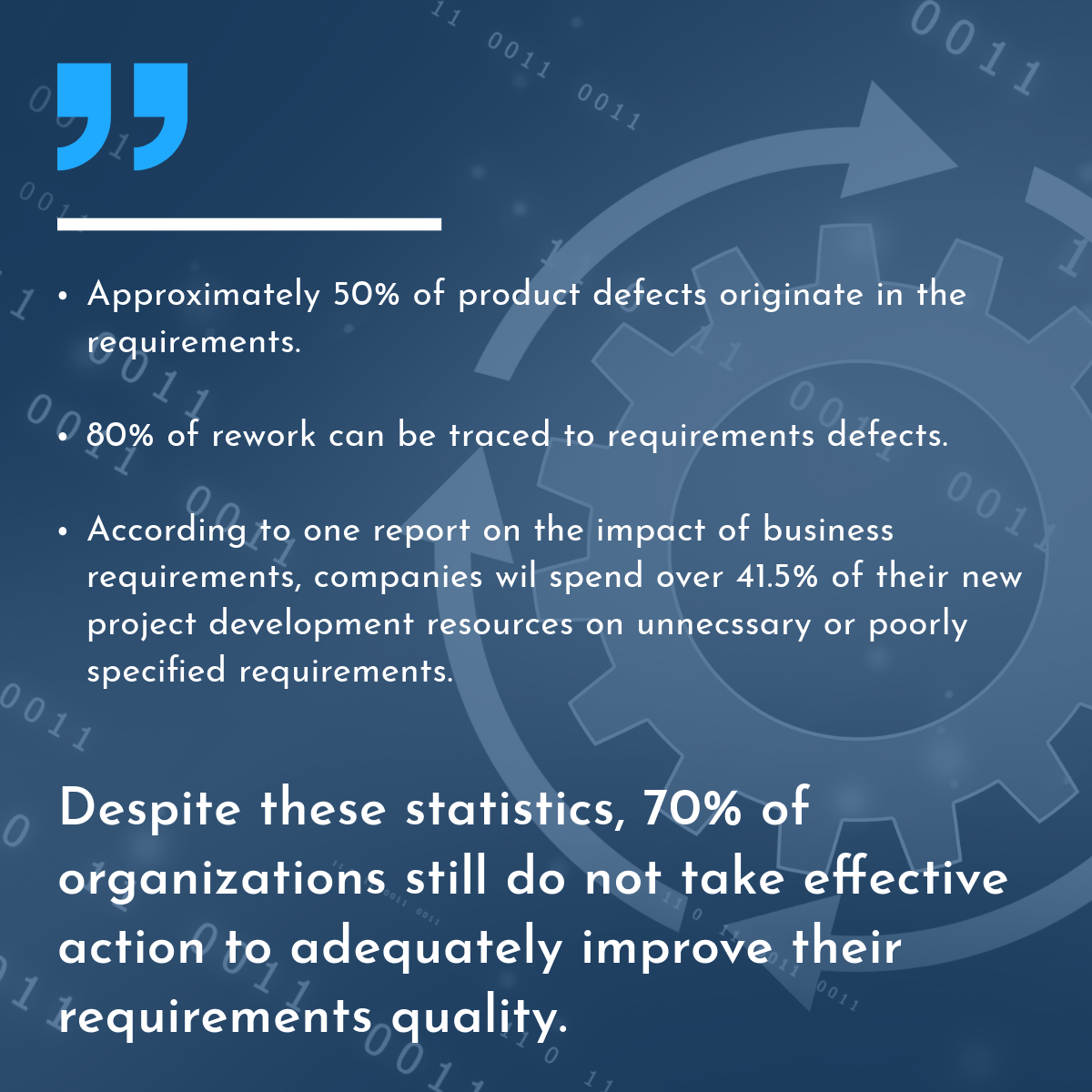
From my own experience, I can tell you that writing and maintaining high-quality requirements is one of the most difficult aspects of project management. At a previous company, I noticed that nearly 30% of Jira issues were barely a few words long—essentially placeholders with no substantial information. Some were empty apart from the title, while others had vague descriptions that left readers guessing about the actual work needed.
This lack of detail has a ripple effect. When developers don’t understand the requirements, they’re forced to make assumptions or spend additional time seeking clarification, which can result in delays, increased costs, and mismatches between what was intended and what was delivered. This issue isn’t unique to user stories; I’ve seen equally poor quality in BRDs and use cases, where critical information like success criteria or edge cases are often neglected.
At the same company, we encountered challenges with our BRDs as well. The document templates were often incomplete, with entire sections missing or lacking essential details. When these gaps weren’t caught in time, they led to rework, scope creep, and frequent project delays. The experience underscored the need for a more systematic approach to ensuring requirements quality—one that AI can now provide. NLP techniques can validate document completeness, as discussed in IBM’s overview of Document AI, supporting comprehensive documentation from the start.
AI-Powered Templates and Structure Enforcement for BRDs
AI tools can help standardize BRD structure by checking for essential components. Rather than relying on manual reviews, these tools can quickly identify when key sections are missing—whether that’s business objectives, success criteria, or risk analysis.
This approach to ensuring completeness echoes the findings of recent research on collaborative methods in requirements documentation. A study on pair documentation practices found that when pairs of document writers worked together, it significantly improved the quality and consistency of requirements. In the same way, an AI-powered tool can serve as a collaborative partner, guiding writers to produce comprehensive and clear requirements documents, potentially transforming individual document creation into a more structured and feedback-driven experience.
Additionally, NLP-driven AI models can analyze the language used within each section of a BRD. This ensures that the document is clear, devoid of jargon, and accessible to all stakeholders, including non-technical readers. The AI could identify vague language—words like “improve performance” or “enhance user experience”—and suggest more specific metrics. Instead of “improve performance,” it might recommend something measurable, like “reduce page load time by 20%.” This aligns with findings from Cheng, Husen, Peralta, et al. “Generative AI for Requirements Engineering: A Systematic Literature Review,” which discusses how AI can detect ambiguities and inconsistencies in requirements documents, leading to more precise and actionable specifications.
Real-World Example: The BRD Completeness Check
In a previous role, I worked on a BRD for a data pipeline project that was riddled with vague language and missing details. The initial document included broad statements like “Optimize data flow for efficiency,” but no specifics on the desired throughput or latency targets. Later, as we progressed, it became clear that stakeholders had different interpretations of what “optimized” meant. With AI, these kinds of ambiguities can be flagged early on, allowing us to clarify and agree on specific targets.
An AI-powered tool could have identified that “Optimize data flow” was insufficiently defined, prompting us to include more specific performance metrics like “achieve 95% efficiency in data throughput under peak loads.” This kind of real-time feedback can prevent costly misalignment down the road.
Guided User Story Writing with AI Feedback
User stories are fundamental in agile environments, but writing effective, actionable user stories requires skill. At a previous company, I saw this firsthand: developers would receive stories like “As a user, I want to access my account” with no additional details on what “access” entailed. This led to confusion and wasted time as developers repeatedly went back to the product owner for clarification.
AI can change this dynamic by acting as a virtual writing assistant, guiding team members in real time as they write user stories. For instance, as someone writes a story, the AI could analyze it to ensure that it follows a consistent structure (e.g., “As a [role], I want to [action], so that [outcome]”). It could flag stories missing a clear outcome or suggest refinements to clarify intent, ensuring that each story aligns with agile best practices.
Recent advancements in AI’s document understanding capabilities, such as those outlined in the DLUE benchmarking framework, highlight how AI can evaluate and enhance text for structural clarity and contextual relevance. For user stories, this means an AI tool could detect when a story is incomplete or vague, offering guidance to ensure that each story is specific and actionable. By referencing similar stories in past projects, the AI could prompt authors to add essential details, such as user roles or permissions, ensuring that stories meet team norms and minimize the need for later clarifications.
Real-Time Suggestions and Best Practices
AI-driven tools can provide immediate feedback to ensure clarity and completeness in user stories. Imagine a tool that analyzes a user story and suggests more specific outcomes based on the context. If a user story reads, “As an administrator, I want to add new users,” the AI could prompt the author to clarify whether this includes setting permissions, sending notifications, or other actions. By building on frameworks like DLUE, such tools can bring greater clarity to the development team and reduce the need for back-and-forth clarifications, ultimately making user stories more actionable and aligned with agile best practices.
Enhancing Use Cases with AI-Driven Enrichment
Use cases help illustrate how a system will interact with users, often detailing specific paths and edge scenarios. However, defining these paths comprehensively is often overlooked in agile environments due to time constraints. AI can aid here by analyzing existing use cases and suggesting additional scenarios that may be relevant.
Take a basic login process: while humans might focus on the main success path, AI tools can methodically identify edge cases that need handling. Password failures, new device logins, and session timeouts are common scenarios that might otherwise be overlooked.
The power of AI to assist in creating diverse and comprehensive content is highlighted in recent research on AI-assisted writing tools. These tools enhance not only the quality but also the range of content, enabling collaborative input that reflects a more complete set of interactions. Applied to use cases, AI-driven enrichment ensures that key edge cases are identified and documented, helping teams to avoid oversights that could impact users post-launch.
Example: Enriching Use Cases with Edge Scenarios
At another organization, we had a project where our use cases primarily focused on the “happy path”—the scenarios where everything goes as expected. However, once we launched, users started reporting issues related to edge cases we hadn’t anticipated, such as sessions timing out or account lockouts. Had we used an AI tool that could recommend edge cases, we would have been better prepared for these scenarios, reducing user frustration and post-launch fixes.
Intent Recognition and Alignment with Business Goals
One of the most valuable capabilities of AI in requirements management is intent recognition. By analyzing the language and context within BRDs, user stories, and use cases, AI tools can determine whether a requirement truly aligns with the project’s overarching business goals. For instance, if a BRD is intended to improve user retention, but the requirements focus on technical metrics unrelated to user experience, AI can flag this misalignment and prompt further review. Recent work on intent recognition models (reference)demonstrates how AI can assess alignment within requirements documentation, making it invaluable for business-focused goals.
This capability ensures that every requirement remains grounded in the project’s purpose. If a user story describes a feature that doesn’t clearly support the project’s objectives, AI could prompt the author to clarify its relevance or consider alternative approaches that better align with the business’s goals.
Practical Impact: Detecting Intent Misalignment in Requirements
In a previous roles, our team spent weeks developing a feature that, in hindsight, did not contribute significantly to the project’s goals. We only realized this after a substantial investment of time and resources, which could have been avoided if we had a way to systematically assess the intent behind each requirement.
With AI, an intent recognition tool could have flagged this feature early on, noting that it didn’t align well with the objectives outlined in the BRD. By prompting us to either clarify its importance or deprioritize it, AI would have saved us both time and resources.
Reducing Ambiguity in Requirements with AI-Enhanced Language Checks
Ambiguity is one of the most common pitfalls in requirements documents. Words like “optimize,” “support,” or “improve” are frequently used but seldom well-defined. In my own work, I’ve seen how these vague terms can lead to confusion and differing interpretations among team members. This is where AI-driven NLP tools can shine, flagging ambiguous language and suggesting alternatives that provide clearer, actionable guidance.
Rather than saying, “The system should support large volumes of data,” an AI tool could suggest specific benchmarks like, “The system should handle up to 1 million records with a response time of under 500 milliseconds.” By refining the language in this way, AI ensures that all stakeholders have a shared understanding of what success looks like.
In addition to NLP, AI-driven document recognition techniques, like those discussed in Forage’s Comprehensive Guide, could help tackle inconsistencies in requirements documents. For instance, these technologies can identify and correct formatting errors or visual irregularities in scanned or imported documents, which is often critical when dealing with complex or high-volume requirements. By leveraging Fourier-based restoration for visual consistency, AI can more accurately interpret misformatted or incomplete requirements, helping to produce documents that are clear and accessible for all team members.
AI-Driven Language Improvement: Ensuring Consistency Across Teams
Another benefit of AI in language refinement is ensuring consistency across different teams. I once worked on a project with multiple development teams, each using slightly different terminology to describe similar concepts. Over time, this led to miscommunications and redundant efforts. AI can standardize terminology across documents, aligning teams and reducing misunderstandings.
If one team describes a data validation process as “checking records” and another refers to it as “data auditing,” an AI tool could prompt them to choose a consistent term. This seemingly small change can have a big impact, improving team collaboration and coherence across project documentation.
AI-Assisted Requirement Reviews and Continuous Improvement
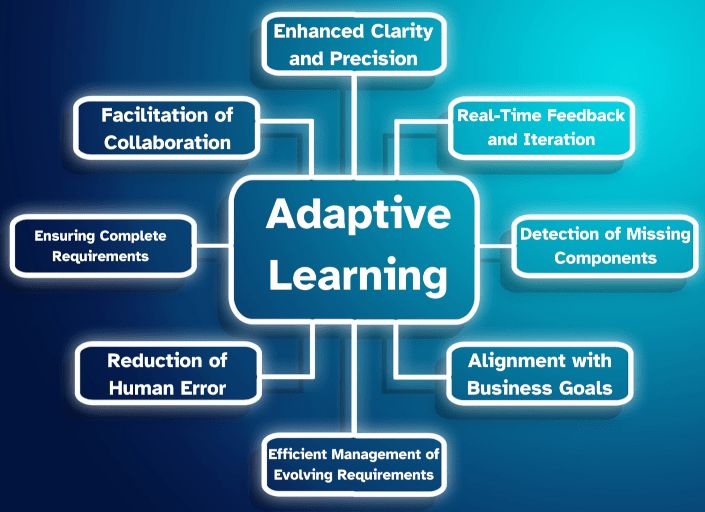
One of AI’s greatest strengths in requirements management is its ability to learn from past projects. By analyzing completed requirements, BRDs, and use cases, AI systems can identify recurring patterns that led to successful outcomes—and those that didn’t. This feedback loop allows AI to refine its recommendations over time, helping teams avoid mistakes they might have otherwise repeated.
An AI tool could review a completed project and pinpoint specific requirements that were frequently misinterpreted, incomplete, or led to development challenges. By incorporating this learning into future projects, the AI can offer suggestions grounded in real-world outcomes, continuously improving the quality of requirements over time.
This approach reflects AI’s capacity for adaptive learning and continuous improvement, where systems learn from experience, integrate feedback, and adjust to evolving requirements. By adopting this methodology, as discussed in this deep dive into adaptive learning, organizations can enhance their requirements management processes and drive more successful project outcomes.
Conclusion: Elevating Requirements Management with AI
The complexity of requirements management is often underestimated. Poorly defined requirements lead to costly mistakes, missed deadlines, and project failures. But by integrating AI into this process, we can enhance the quality, clarity, and alignment of BRDs, user stories, and use cases.
Through real-time feedback, structured guidance, intent recognition, and continuous learning, AI has the potential to transform how we approach requirements. It’s not just a tool for speeding up documentation; it’s a partner in ensuring that every requirement supports the project’s business goals and provides clear, actionable instructions for development teams.
In our next part, we’ll explore how AI can further streamline project management workflows, specifically focusing on agile reporting and progress tracking. For now, it’s clear that with AI on our side, we have an opportunity to improve requirements management from the ground up, moving from vague, incomplete documents to precise, business-aligned requirements that drive project success.
More on SimplemindedBot
For more insights on AI-enhanced requirements and project management, check out these related posts:
Writing User Stories With AI 1: Introduction: Provides foundational knowledge about using AI to generate user stories, directly complementing the requirements improvement process discussed in this article.
Writing User Stories With AI 2: Fine-Tuning Your Prompt: Explores how to craft effective prompts for AI when generating user stories, which is crucial for improving requirements documentation quality.
Writing User Stories With AI 3: Beyond User Stories: Discusses advanced techniques like Gherkin and sequence diagrams that enhance requirements clarity, building on the concepts covered in this article.
Critically Evaluating AI-Generated Content: Essential reading for understanding how to assess and validate AI-generated requirements documentation, ensuring quality and accuracy.
AI-Enhanced Agile DoD: Improving Agile Workflows with AI: Shows how AI can improve the Definition of Done process, which is closely related to requirements management and quality assurance.
Using AI for Retrospective Analysis in Agile: Demonstrates how AI can help teams learn from past projects to improve future requirements documentation.
GIGO in Project Management: Explores the broader context of how AI can improve project management inputs, including requirements documentation.
Harnessing AI to Tame Knowledge Chaos in Agile Teams: Discusses AI’s role in managing project knowledge, which is crucial for maintaining high-quality requirements documentation.
These articles provide additional perspectives on using AI to enhance various aspects of project documentation and management, helping teams create more effective and actionable requirements.